Stepped enterosorption in the complex therapy of allergic dermatoses
E. Murzyna · A. Lytus
Department of Dermatovenerology, NMAPE named after P. L. Shupik, Kyiv
Stepwise enterosorption in complex therapy of allergic dermatoses
"Medicine there is addition and subtraction.
Taking away what is superfluous, adding what is missing. And whoever can do it best is the best doctor..."
In dermatological practice, the expression of Hippocrates is especially relevant in the treatment of allergic dermatoses. The basis of these diseases lies in the changed reactivity of the body, in particular the skin, in relation to exogenous and endogenous irritants - food, medicinal, chemical, household and professional. Also, violations of the barrier function of internal organs in accompanying chronic diseases facilitate the entry into the body of exoallergens of various nature (medicines, dust, food products, etc.), xenobiotics of industrial origin, and the processes of detoxification and elimination of these foreign substances from the body also change. The accumulation of these ingredients in the body leads to the development or exacerbation of manifested allergic dermatosis.
Removal of foreign substances that enter it from the environment, or toxic metabolic products formed in the body itself, can be achieved by methods of efferent therapy - from the Latin "efferens" - removes - a set of active detoxification methods aimed at stopping the action and removing from the body toxic substances, endogenous and exogenous toxins, poisons, chemicals, aggressive enzymes, foreign proteins and the like. This can be done by hemodilution, vulnerosorption, ultrahemofiltration, peritoneal dialysis, extracorporeal blood oxidation or enterosorption.
Preparations that carry out such elimination - enterosorbents - drugs of various structures that bind exo- and endogenous substances in the gastrointestinal tract by adsorption, absorption, ion exchange, complex formation.
Enterosorption is a traditional method of efferent therapy. But it has advantages over other methods of removing foreign substances from the body due to the absence of the need for surgical intervention on blood vessels and the associated risk of possible complications, the absence of a direct damaging effect on biological fluids (blood, lymph), ease of use and the possibility of wide use in outpatient treatment, in the field and at home, during training and competition; complete absence of contraindications and side effects. Enterosorption for a long time had limited use, since the sorbents available at that time showed low efficiency, required high dosages, and did not meet the requirements of selectivity. The efficiency of enterosorption directly depends on the quality of the sorbents used.
The action of enterosorbents when entering the body includes several interrelated stages - direct and indirect. The process includes adsorption and removal from the body of toxic substances that are formed directly in the intestines; binding of toxic substances entering the intestinal lumen from the blood, and thus preventing their reabsorption; cleaning of digestive juices containing a significant amount of toxic substances; modification of lipid and amino acid spectra of intestinal contents due to selective sorption of some amino acids, free fatty acids; biotransformation of highly toxic products into less toxic or even non-toxic substances.
In addition, the elimination of toxic substances formed in the intestine has a positive effect on the liver, kidneys, improving their functional state, as well as the activity of the cardiovascular system. This is due to the well-known ability of toxic metabolites, primarily molecules of medium molecular weight, so-called medium molecules, to destructure or significantly disrupt the functional state of the plasma membrane of hepato- and cardiocytes, erythrocytes, and other cells.
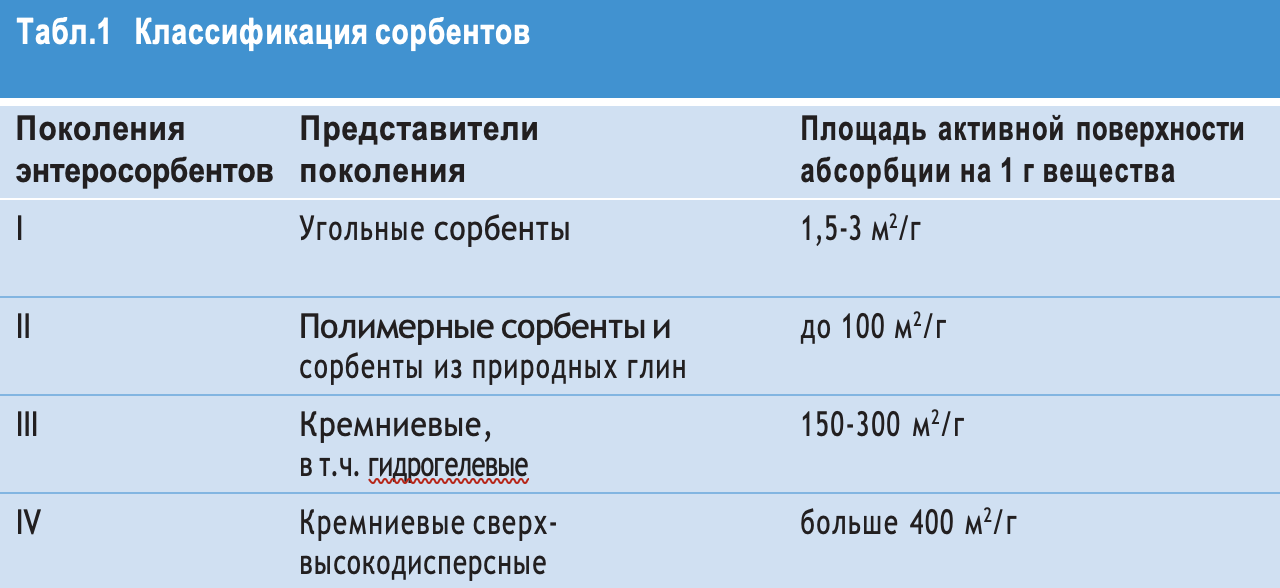
There is no clear classification of enterosorbents. From generation to generation, they are distinguished by more and more advanced and diverse adsorption properties, as well as additional, not only sorption, but also so-called mediated healing effects. From generation to generation, the active surface area of enterosorbents increases. Non-porous sorbents of the 4th generation have the maximum sorption area. At the same time, the entire surface area is active. Consequently, the daily dose of enterosorbents is reduced.
Enterosorbents are divided into the following groups: carbon sorbents based on activated carbon, granulated coal, carbon fiber materials; ion-exchange materials or resins; natural food fibers; other enterosorbents (clays, zeolites, Almagel, silica gels).
Other classifications of enterosorbents are also accepted: by dosage form - granules (coal), powders (carbolene, cholestyramine, povidone), tablets, pastes, food additives (pectins, chitin).
According to the chemical structure - activated carbon, aluminosilicates, aluminogel, sorbents of oxidizing, organomineral and composition, food fibers.
According to the mechanism of sorption - adsorbents, absorbents, ion-exchange materials, sorbents with catabolic properties, sorbents with combined mechanisms.
By selectivity - selective, mono-, bi-, polyfunctional, non-selective (activated carbon, natural preparations - lignin, chitin, cellulose).
By type of substance registration – dietary supplements and pharmacological preparations.
Also, the classification of sorbents is carried out according to evolution (Table 1).
The following requirements are imposed on modern enterosorbents:
- Absence of a damaging effect on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Good evacuation from the stomach;
- High sorption capacity;
- Beneficial influence on gastrointestinal secretion and biocenosis of microflora of digestive organs;
- Convenient form and ease of dosing;
- Absence of negative organoleptic properties of the sorbent (including aromatic additives).
Table 1 Classification sorbents
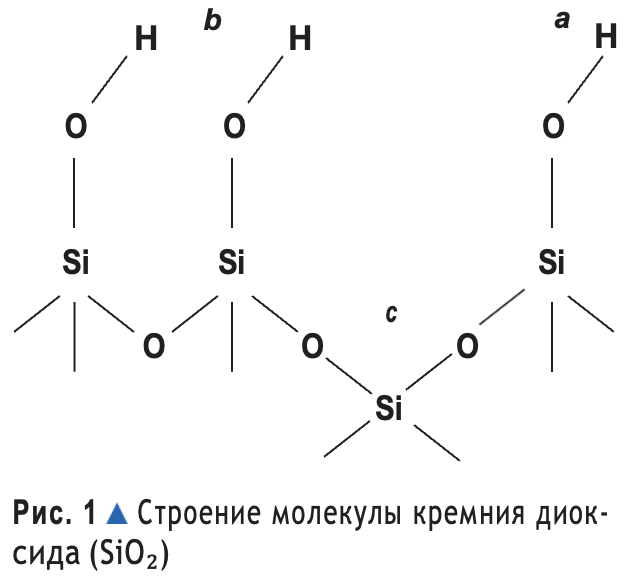
A real breakthrough in enterosorption was the unique development of domestic scientists - a compound of highly dispersed silicon dioxide, which in terms of its sorption properties is tens of times superior to all existing sorbents, and the speed of action and selectivity complement the unique properties of the molecule (Fig. 1), they allow to remove edema, heal wounds locally. Silicon dioxide promotes transportation from the internal environment of the body (blood, lymph) to the gastrointestinal tract and the removal of various toxic products, including: alkaloids, glycosides, salts of heavy metals, organophosphorus and organochlorine compounds, barbiturates, ethyl alcohol and products of its metabolism; biologically active substances associated with the processes of allergy and inflammation (prostaglandins, serotonin, histamine), metabolic products (urea, creatinine, final nitrogen), lipids. Silicon dioxide contributes to the reduction of the metabolic load on detoxification organs (primarily the liver and kidneys), elimination of the imbalance of biologically active substances in the body, correction of metabolic processes and immune status, improvement of lipid metabolism indicators such as cholesterol, triglycerides and total lipids.
The unique production of highly dispersed silicon dioxide was founded at the Orysil-Pharm plant in 2005 in Kalush, Ukraine, under the Atoxyl brand. The only plant in the territory of Eastern Europe and Asia, which produces highly dispersed silicon dioxide according to the original method. There are only three such factories in the world.
The raw material for the production of Atoxyl is silicon oxide, which, as a result of original processing at a temperature of 2000°C, acquires the appearance of microspherical particles. Upon entering water, the particles attach hydroxyl groups of water to themselves and form an original spatial structure with a strong electrostatic charge, which is the reason for the high speed of sorption. In 4-5 minutes, 80% absorbs toxic substances, which provides a quick therapeutic effect and clinical result.
Silicon dioxide manufactured by Orisyl-Pharm has passed the FDA and USA Pharmacopoeia tests according to USP 29-NF24 monograph tests, does not absorb water, vitamins and microelements, and even with long-term use, does not cause changes in the electrolyte composition of the body. It allows to combine therapy with other drugs, as it quickly fills its sorption capacity.
Thus, fulfilling the first commandment of Hippocrates in the treatment of allergic dermatoses, we do not leave the second component "adding the missing one". It is reliably known that patients with allergic dermatoses have a violation of intestinal microbiocenosis, which is accompanied by the absence or sharp decrease in the number of bifidobacteria, colonization of enteropathogenic hemolyzing E.coli and impaired production of IgA by the intestine.
From the modern point of view, the normal intestinal microflora can be considered as a set of indigenous microorganisms that constantly populate the digestive tract and represent a non-specific barrier of protection against pathogenic bacteria and other exogenous factors of aggression. Under the conditions of a normal physiological state, the relationship between "macroorganism and microflora" has a symbiotic character, while the microorganisms inhabiting the human gastrointestinal tract perform a variety of vital functions, including the processes of digestion and absorption, intestinal trophicity, the synthesis of vitamins, enzymes, amino acids, have a bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect on pathogenic microflora, provide anti-infective protection and immunoregulatory function, participate in the synthesis class A immunoglobulins, natural antibodies, in the morphogenesis of the immune system.
Representatives of the normal microflora of the intestine - bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, lactococci, propionic acid bacteria - have high immunogenic properties, which are manifested primarily in the support of the concentration of secretory IgA on the mucous membrane (not only the intestine), regulation of the maturation of the lymphoid apparatus of the intestine, and the generalization of the immune response. In turn, the immune system is a regulator of maintaining the balance of intestinal microbiocenosis. According to the postulates of microbiological medicine, all drugs affecting intestinal microflora (beneficial) are divided into three types: prebiotics, probiotics and symbiotics.
Prebiotics are indigestible food ingredients that stimulate the growth and metabolic activity of one or more groups of native bacteria (lacto- and bifidobacteria) in the large intestine. There is a large number of bifidogenic factors that stimulate the growth of their own intestinal microflora (antioxidants, unsaturated fatty acids, organic acids, oligo-, mono-, polysaccharides, peptides, enzymes, etc.). The main component of the prebiotic component of functional nutrition is dietary fiber - the sum of polysaccharides and lignin, which are not digested by the endogenous secretions of the human gastrointestinal tract. One of the most important effects of dietary fiber is the improvement of the digestive function of the body and the formation of healthy intestinal microflora.
Synthetic prebiotics include lactulose. In the small intestine, there are no disaccharidases for its hydrolysis, therefore lactulose enters the large intestine practically unchanged, where it undergoes bacterial hydrolysis with the formation of monosaccharides and short fatty acids. Under the action of lactulose, the intra-intestinal pH level decreases in the acidic direction. An acidic environment inhibits the growth of pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria, and also ensures optimal action of digestive enzymes. Due to the formation of short-chain fatty acids, lactulose provides protection and regeneration of the intestinal mucosa, restores the permeability of the intestinal wall caused by enterotoxins; increases the osmotic pressure of the intestinal contents, which leads to fluid retention in it; activates peristalsis; there is an increase in the saccharolytic intestinal microflora. Therefore, the use of prebiotics in the complex treatment of allergic dermatoses is justified and shown from the standpoint of normalizing the state of intestinal microflora.
The company "Orisil-Pharm" has developed a modern drug based on selective highly dispersed silicon dioxide and natural prebiotic lactulose - Eliminal Gel, which, thanks to its complex composition, has a detoxifying, immunomodulating and restorative effect, promotes rapid colonization of the intestines with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, activates the processes of growth and restoration of its own protective intestinal microflora, helps to correct the balance and composition of normal intestinal microflora.
The Department of Dermatovenerology of the P.L. National Academy of Medical Sciences Shupyk, on the basis of the Kyiv City Clinical Dermatology and Venereology Hospital, which is the clinical base of the department, clinical observations of the use of the drug "Atoxyl" and "Eliminal Gel" in the complex therapy of children with allergic dermatoses were carried out. The drugs were provided to the hospital as humanitarian aid.
Research materials and methods
20 children with allergic dermatoses, aged from 6 to 17 years (average age – 11.7±0.76 years), participated in the clinical observation. Among them: there were 14 children with atopic dermatitis, 1 with eczema, and 5 with allergic dermatitis.
"Atoxyl" and "Eliminal Gel" were added to the complex traditional therapy, which included systemic and topical preparations. "Atoxyl" was prescribed 1 vial per day in 3 doses 1.5 hours before meals - 3 days, then "Elimin Gel" was prescribed - for 10 days 1.5 hours before meals, 1 stick 2 times a day for children under the age of 13, 1 stick 3 times a day for children aged 14–17 years. To objectively assess the severity of the disease before and after treatment, in children with atopic dermatitis and eczema, we used a quantitative assessment - the SCORAD coefficient (kS), which was calculated by estimating the area of skin damage (A); the degree of manifested (B) (erythema, formation of papules/vesicles, wetness, excoriations, lichenification, dry skin) and subjective (C) (itching of the skin and sleep disturbances) symptoms. With the maximum prevalence of the process and the manifestation of objective and subjective symptoms, SCORAD = 103, and with their complete absence, SCORAD = 0.
According to the severity of each process, the value of the SCORAD coefficient (kS) can be conditionally divided: 0 ≤ kS ≤ 30 – mild degree, 31 ≤ kS ≤ 60 – medium degree, kS > 61 – severe degree of disease.
The SCORAD coefficient (kS) was calculated by the computer program "SCORAD Calculator" of the Belgian company "AIIS" (USB Pharmar - 1997).
According to the efficiency parameters oftreatment of allergic children dermatitis, were taken assessment dynamics values (here 0– "absence"et" to 3 - "very strongly expressed") of the following symptoms: papules/shellsshenie, hyperemia, itching.
Research results
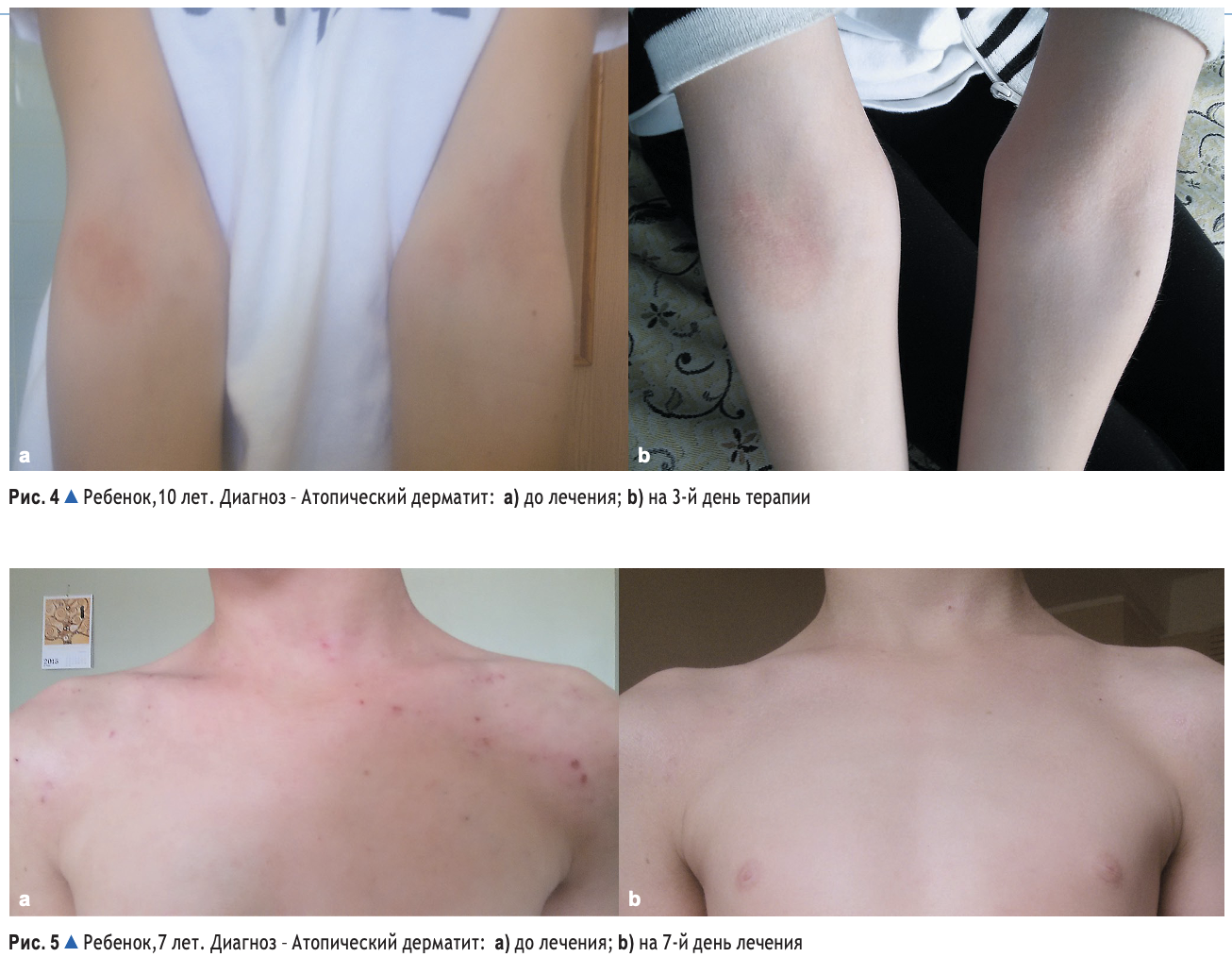
In children with atopic dermatitis and eczema, who received therapy with Atoxyl and Eliminal Gel, we noted positive dynamics in the clinical manifestations of the disease (Figs. 2–5). This occurred in the reduction of infiltration and hyperemia in the lesions, the involution of papular rashes and the shedding of crusts, the reduction of itching and the normalization of sleep, already in the first 3 days of using the drug. On average, the SCORAD coefficient was 35.57 ± 3.54 before treatment in observed children with manifestations of atopic dermatitis, a disease of mild and moderate severity. After 10-14 days of treatment, the SCORAD coefficient decreased on average to 10.61 ± 0.82. The pathological process was completely resolved during therapy in 14 of 15 children. In one child, we observed repeated exacerbation of the pathological process as a result of a gross violation of the hypoallergenic diet.
Significant results of therapy in children with allergic dermatitis using Atoxyl and Eliminal Gel became noticeable after 3 days of therapy. And if before the beginning of the treatment, the average value of papular rash was estimated at 2.60 ± 0.24, hyperemia – 1.60 ± 0.24, and itching was equal to 3, then in the course of further therapy the rating decreased from 3 (“very strongly expressed”) to 0 (“absent”). In 80% patients (4 out of 5), clinical manifestations of dermatitis were completely absent on the 7th day of using the drug "Eliminal Gel", and in one patient the pathological process was completely resolved on the 13th day of therapy.
The effectiveness of the therapy was evaluated according to the following parameters: clinical remission (clinical recovery), significant improvement, improvement, no effect. Summarizing the results of 3-day use of Atoxyl and 10-day Eliminal Gel in the complex therapy of children with atopic dermatitis and eczema, we found clinical remission in 12 children (80,00%) with atopic dermatitis and 1 child with eczema; significant improvement of the condition – in 1 child with atopic dermatitis. In 1 boy (6.67%), a repeated worsening of the pathological process was observed due to a gross violation of the diet, we attributed this condition to the assessment of effectiveness - "no changes". But the repeated appointment, with the purpose of detoxification and removal of harmful substances from the body, significantly eased the general condition of the child and contributed to the speedy resolution of the pathological process. In all 5 children with allergic dermatitis, we observed clinical recovery (100,00%). All patients assessed the tolerability of Atoxyl and Eliminal Gel as "very good" or "good". There were no cases of children refusing to take the drug due to negative organoleptic properties.
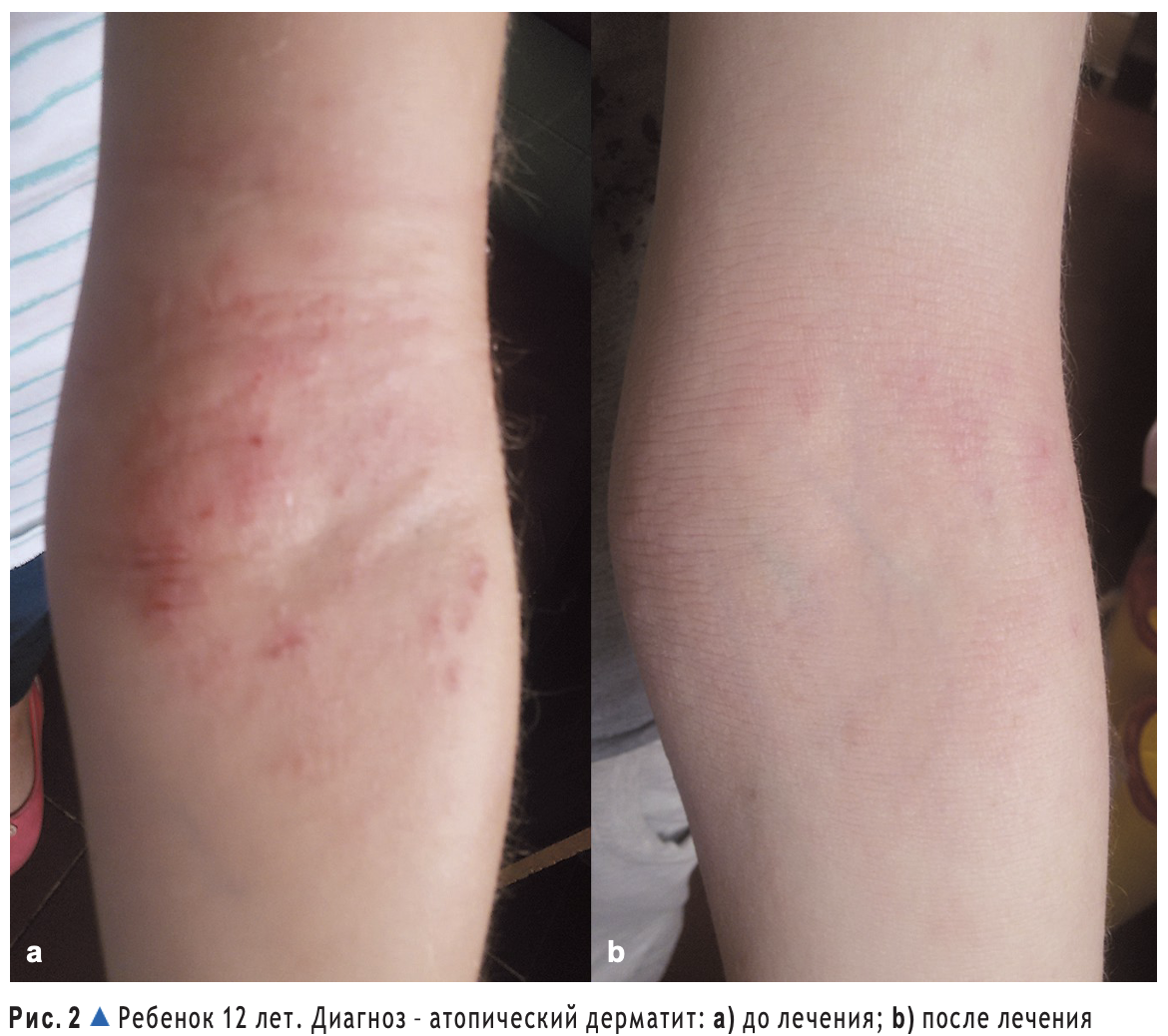
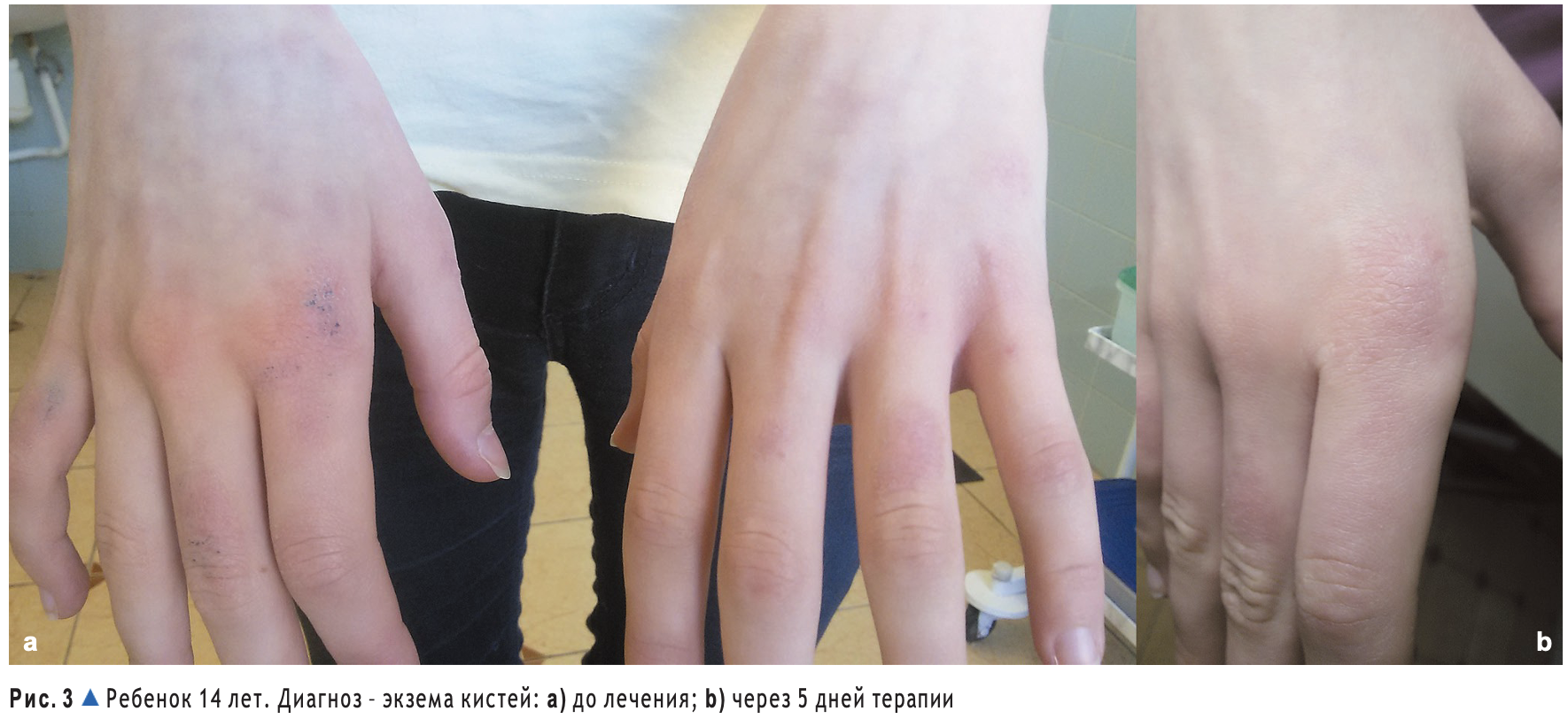
Practical conclusions
The use of enterosorbents and drugs that normalize the state of normal intestinal microflora in the complex therapy of allergic dermatoses is reasonable and effective. Modern domestic drugs "Atoxyl" and "Eliminal Gel", containing silicon dioxide as an enterosorbent and prebiotic lactulose, contribute to the rapid removal of endo- and exotoxins from the body, which caused the exacerbation of the pathological process or provoked the onset of the disease, and led to the correction of the balance and composition of the normal intestinal microflora. This is a reflectionmoose on the state of the clinical cardny: to the quick solution of clinical problems manifested by a pathological process, normalization of sleep and reduction of itching in patients. This makes it possible to quickly improve the quality of life not only of young patients, but also of their parents.
Address for correspondence
E. Murzyna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Dermatovenerology, P. L. Shupyk National Academy of Medical Sciences
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Literature
- Skin diseases in children: translated from English / D. Abek, V. Burgdorf, H. Kremer - M.: Med. Lit. – – 160 p.
- Belyakov N. A., Solomennikov A. V. Enterosorption — mechanism of therapeutic action //Efferent therapy. 1997, vol. 3, No. 2.
- Korotky N. G., Tikhomirov A. A. et al. Atopic dermatitis in children. Tver: Triada, 238 p.
- Kutasevich Ya.F. Principles of treatment of atopic dermatitis // Clinical Immunology, Allergology, Infectology. – – No. 3/1. – P. 37-45.
- Mavrov I.Y., Bolotnaya L.A., Serbina I.M. Fundamentals of diagnosis of treatment in dermatology and venereology // Handbook for doctors, interns and students. Kh.: Fact, - 792 p.
- Nikolaev V. G. and others. Enterosorption: the state of the question and prospects for the future // Bulletin of the problems of biology and medicine. No. 4, p. 7–17.
- Nikolaev V. G., Guryna N. M. Enterosorption today: sorption materials and mechanism of action. Electron. resource URL: http://kiulong.cjm. ua/content/view/66/58/
- Paliy I.G., Reznychenko I.G. Modern view of the problem of enterosorption: selection of the optimal drug. News of medicine and pharmacy. 2007; 11:
- Ursova N. I., Gorelov A. V. Modern view of the problem of enterosorption. Optimal approach to drug selection. RMZh. 2006; 19: 1391-1396.
